By Dr. Dhanalakshmi N.
Ph.D. (N), PG Psychological Counselling, M.Sc. Psychology
Introduction
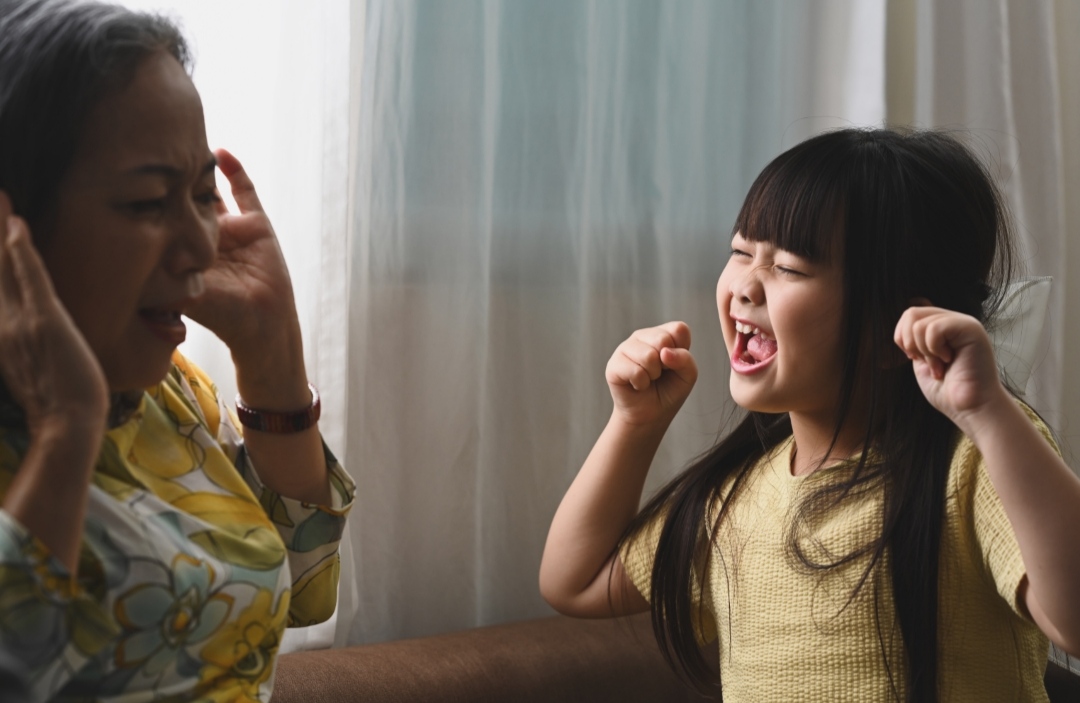
Parenting is an art. Every parent loves their children and yet, we all had experienced losing our temper sometimes. It is important to practice patience daily while caring for our children because children imitate by observing us. Practicing patience will benefit our health, family and other people around us.
The following are some strategies for parents to practice patience while caring for their children:
- Identify triggers: Identify the factors causing you to lose your patience. Finding the cause will help you to prevent the triggers or solve the problem.
- Self-care: Caring for children and managing their daily activities may be stressful at times. It is important for the parents to care for them with a nutritious diet, adequate sleep, exercise, yoga, meditation and relaxation techniques that will promote their physical and mental well-being and also helps to manage their emotions appropriately. Set a time for yourself.
- Practice patience: Whenever you feel stressed and frustrated, consciously calm down and think twice before you answer or speak to your child. Whenever you are angry, practice counting from one to ten before you answer your child. Avoid raising your voice, hitting, shouting or screaming etc.
- Practice breathing: Sit in a comfortable place, close your eyes, begin with a few normal breaths and followed by deep breaths, breathing deeply through the nose and breathing out through the mouth. Focus on breaths while practicing. Practice 10 to 20 minutes daily. While breathing relax your muscles and body.
- Practice mindfulness techniques: Live in the present moment. Living in the past makes you depressed and living in the future will lead to anxiousness. Live in the present moment by mindful eating, mindful bathing, mindful talking, mindful breathing, mindful working etc., being aware of every activity will promote satisfaction and balance your emotions. For example, feel the color, texture and taste of the food while eating than eating food by watching TV or phone.
- Practice Gratitude Journal: Set a regular time to record three to five things for which you feel grateful. Write down an inspiring person, good experiences, happy moments, and blessings etc., Daily practice of a gratitude journal promotes a good mood, positive emotions, satisfaction with life and develops patience.
- Practice listening skills: Listen to your child before you respond or react to your child’s behaviour. Ask your child to explain her behaviour or the reason for her behaviour, this will help the parents to understand the child from her perspective.
- Practice kindness: Practice kindness. One who is kind to self will be kind to others. Practicing kindness helps you to develop patience. Being kind to self and others reduces the secretion of stress hormone(cortisol) and promotes self-confidence and compassion.
- Assess the child’s needs: Assess the child’s needs frequently and meeting the needs will prevent stress and frustration for the child and also for the parents. Making a schedule from waking to bedtime will prevent confusion and minimizes stress.
- Work-life balance: Plan for a fun day. Spend time together with your child, relax and enjoy playing some fun games, sharing some stories, doing art and craft work, taking a short walk or planning for a picnic etc., setting time for having fun daily promotes happy hormones and balances your emotions. Daily we have the opportunity to practice patience
Conclusion
Patience is important in our daily life. Practicing the above strategies will help as the key factor to developing patience at home, office and while waiting at a traffic signal etc., Daily practice will help parents to develop patience.